Loop systems
This section includes equipment that can help a user to hear conversation and sound within a room. Loop systems are designed to be hearing aid compatible, hearing aid receivers can be used by hearing aid users and/or non-hearing aid users.
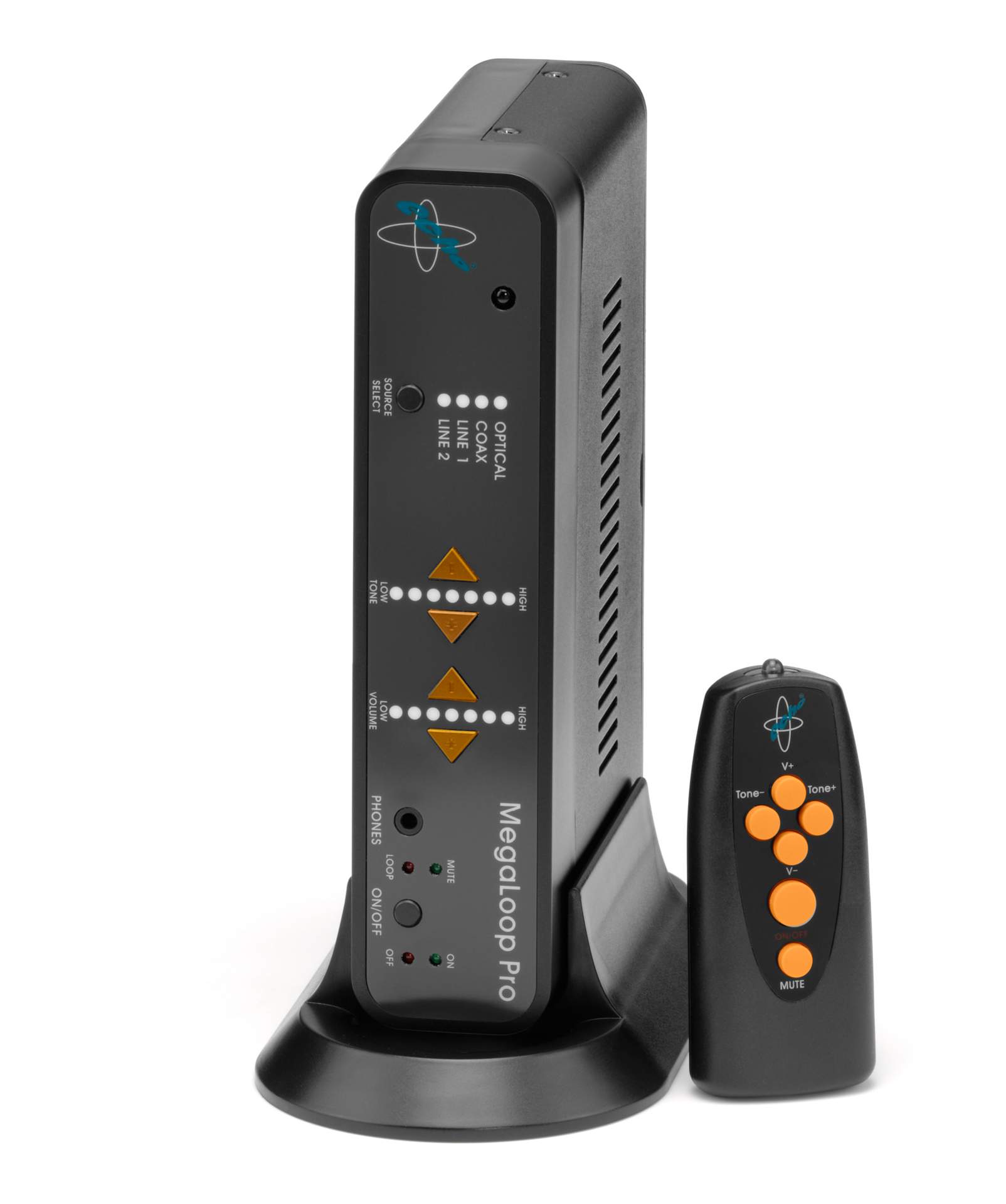
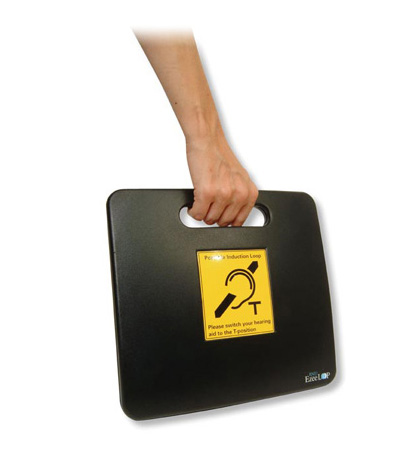
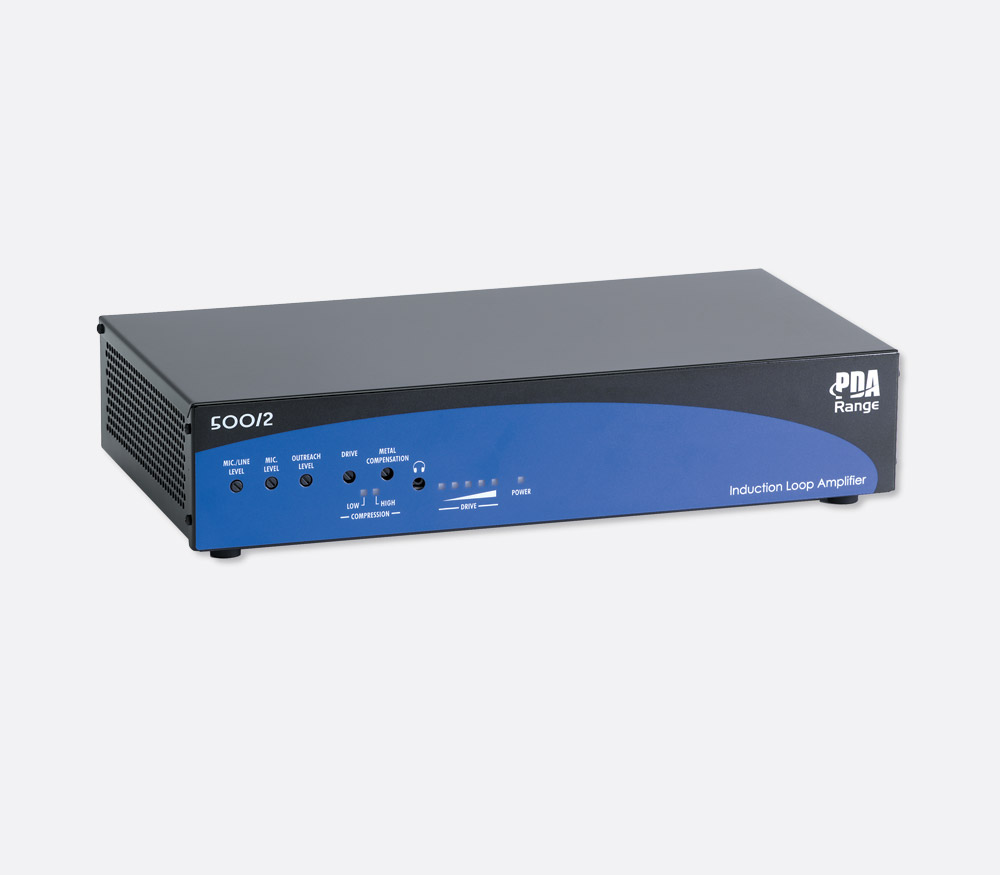
Home and public use loop systems include a cable which is placed around the area (often around the whole room) in which the user or guests/customers will be when listening to the transmitted sound. The loop transmits the sound to the user as a magnetic field which is received by hearing aids with a loop (T) setting. If the user wears a hearing aid an induction loop may help them to hear sounds with more clarity and reduce the effect of background noise. As the user is not wired to any device they can walk around and listen from anywhere within the loop.
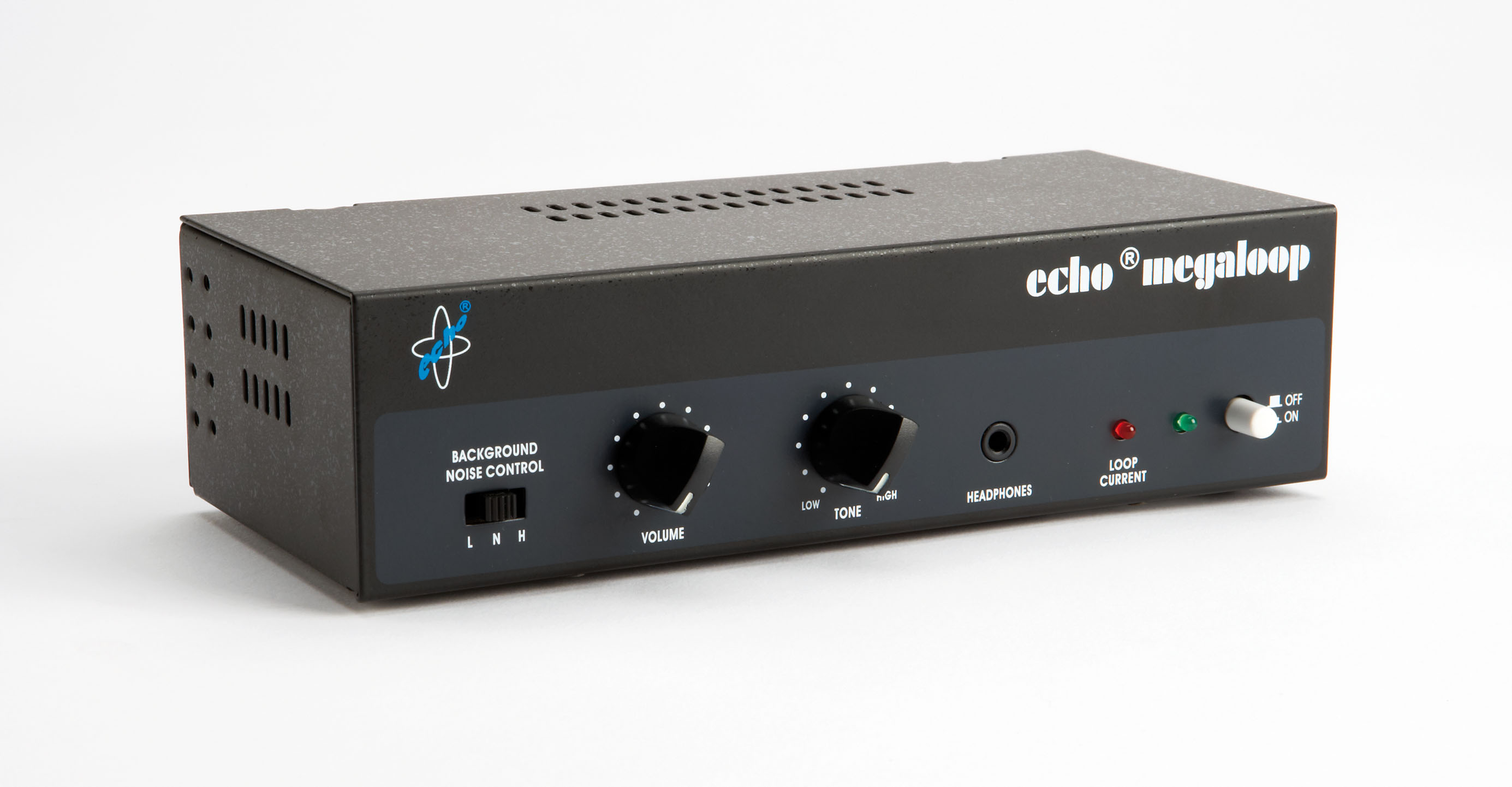
Home loop systems can be used to hear conversations or sound from the user’s television or music players, public use loop systems are designed for use in public buildings, meeting rooms, conference centres and at counters e.g. in banks and post offices.
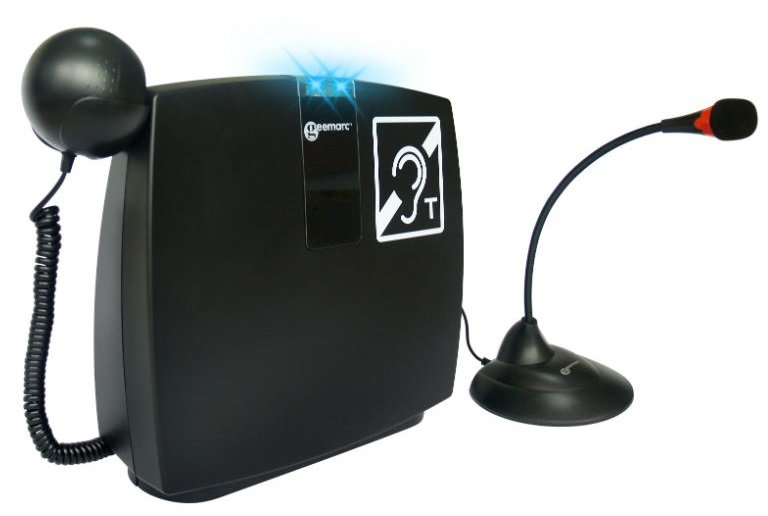
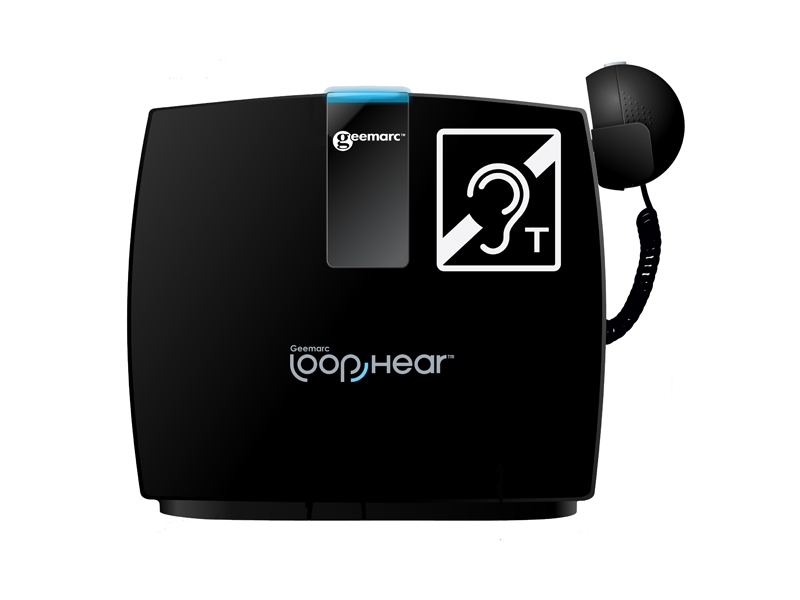
Portable desktop loop systems are designed for use at a desk with the speaker/s sat on one side and the hearing aid user, who wishes to hear the speaker, sat on the other side. The systems either have a built in microphone or a socket to plug a microphone into. The desktop unit transmits the sound to the user as a magnetic field which is received by hearing aids with a loop (T) setting. If the user wears a hearing aid an induction loop may help them to hear the speaker with more clarity and reduce the effect of background noise.
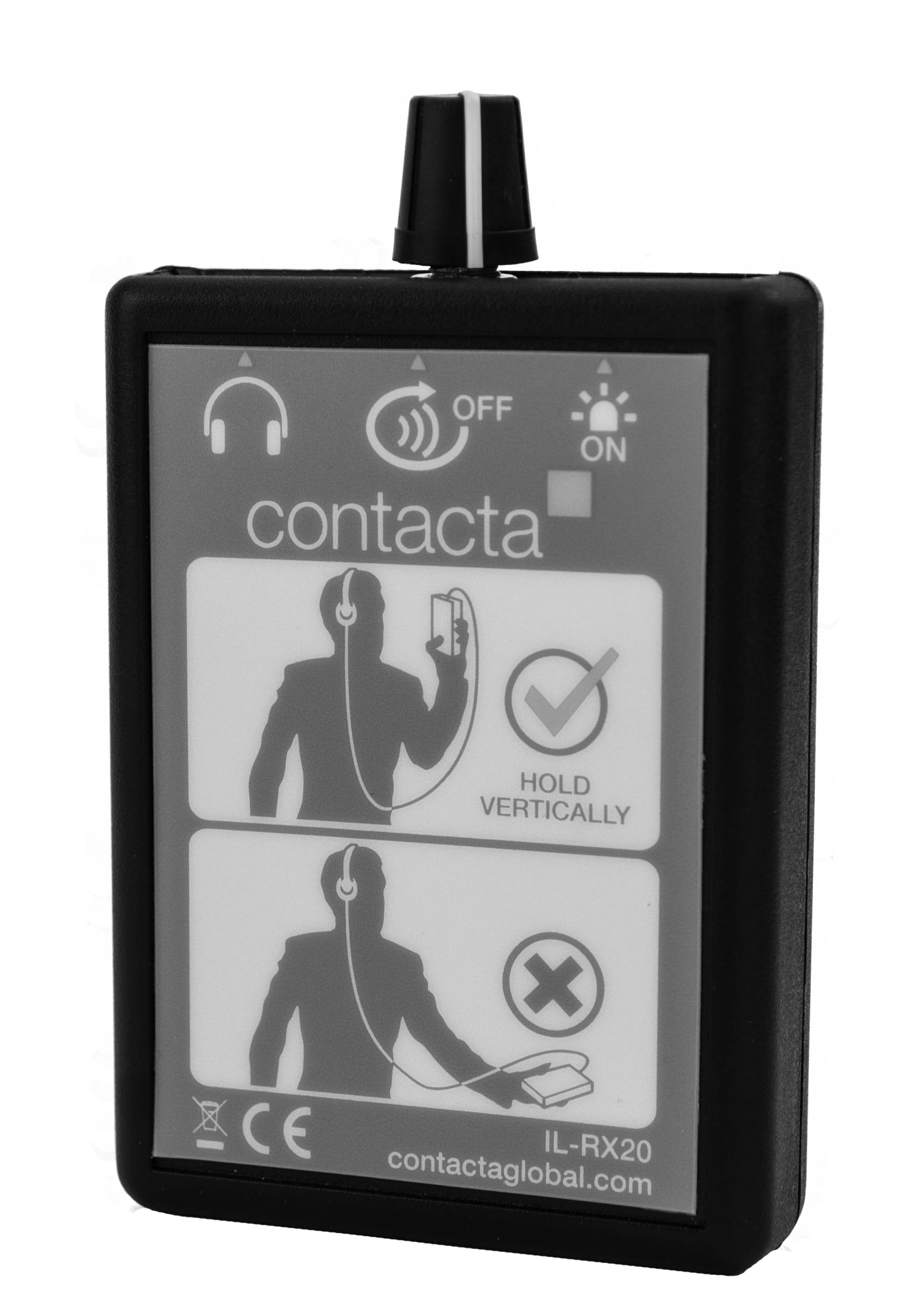
Induction loop receivers are designed for individuals with some hearing loss who do not use a 'T' position hearing aid but would like to use induction loop systems. The receiver picks up the magnetic field from a loop system and converts it into sound which, depending on the model, you hear through headphones, earphones or stetoclips.
Car system loops enable the user to hear conversations or listen to music or the radio while in a car.
Introduction
There is a large choice of equipment and an increasing amount of technology available to help with communication if you are blind or have low vision. This ranges from handheld magnifiers to machines which automatically convert written text to speech, and apps for telephones or tablet devices.
If you have not already done so, we recommend that you have an eye test. An eye test can help detect any eye conditions before you notice the effect on your sight and early treatment may prevent your sight from getting worse. Everyone should have their eyes examined by an optician every two years. If you cannot get to a high street optician because a disability prevents you from leaving your home, you may be entitled to an eye examination at home. You can search for your nearest optician on the NHS Choices website.
If your vision suddenly deteriorates or you have severe pain in your eyes attend your local accident and emergency department as soon as possible.
A low vision assessment can identify a specific type of sight loss such as macular degeneration, glaucoma or Retinitis Pigmentosa. Low vision service provision varies across the country.
Magnifiers
If you have low vision, magnifiers may help by enlarging reading and writing materials. These may include labels, instructions, controls, correspondence, books and magazines. Using the wrong magnifier for a significant period of time can cause eye fatigue and physical problems.
Before buying a magnifier consider the magnification and size of the lens. Generally, a larger magnifier will have lower magnification and a high-powered magnifier will have a small lens. Higher magnification magnifiers tend to show you less of what you are looking at, perhaps only a word or a few letters at a time. Low vision training may help you make the most of a magnifier, especially if you are experiencing the symptoms of macular degeneration which causes a loss of central vision, glaucoma or Retinitis Pigmentosa.
Hand-held magnifiers
These devices can be used for most everyday needs and are held directly over the object to make it appear larger. The strength of magnification may vary between about 1.5 times (x 1.5) to 12 times (x 12). They are available in a range of physical shapes and sizes. How much bigger you see the item will also depend on the distance you and the magnifier are from the object you are looking at.
Some hand-held magnifiers are fitted with a built-in battery powered lamp or LED to improve lighting and enhance the text.
Hand-held magnifiers are not suitable if you have a shaky hand or find a handheld device difficult to grip and as they are held close to the page they are generally unsuitable for use when writing.
Magnifiers with built-in lighting
Hand-held optical magnifiers are available with built-in lighting from a bulb or LED to help illuminate the area being viewed. Some are available with lighting of different colour temperatures. These colour temperatures are described in Kelvin or K. A lower number (e.g. 2,700K) emits a more yellow light, a higher number (e.g. 6,000K) emits a whiter light.
A study in 2012 suggested that individuals who chose magnifiers with their preferred colour temperature found the magnified image clearer and could read faster than if they used a magnifier with a colour temperature they did not like. If you are thinking of purchasing an illuminated magnifier it may be worth trying models with different colour temperatures to find out which you prefer.
Hands-free magnifiers
Magnifiers with neck cord attachment
These products have a neck cord or attachment which enables the magnifier to rest on the chest leaving the hands free. Some incorporate a second inset lens, giving greater magnification.
Magnifiers attached to spectacle or headband
These magnifiers are built into a spectacle frame and attach or clip to existing spectacles or are supported on a headband. Some lenses are designed to flip away from the eyes when not in use. It is advisable to seek the opinion of a qualified ophthalmologist before additional magnification is added to prescription lenses.
Magnifiers with a stand used directly on or over the subject
If you have weak or shaky hands, using a magnifier on a stand may be ideal for reading and, if the stand is tall enough, also for writing.
Some of these magnifiers have an integral light. However, some users find it difficult to find the start of the text they wish to magnify when using a stand magnifier.
Magnifiers mounted or placed on furniture, floor or wall
These magnifiers are designed to be either wall-mounted, attached to furniture by clamp, or free standing on a table-top or floor. They facilitate hands-free use.
Many are mounted on an adjustable arm allowing variation of angle and position. Some incorporate a light.
Magnifiers to fit over screens
Magnifying equipment included in this section is designed to be attached externally over a TV or computer screen.
Bar, dome and sheet magnifiers
Similar to stand magnifiers, these may be particularly suitable if you have reduced grip or shaky hands which make holding a handheld magnifier difficult. However, magnifiers used directly on the page can only be used for reading as there is no room for a pen to be placed underneath.
Dome magnifiers can help to focus available light which helps make the magnified text appear bright. Bar magnifiers focus on one or two lines of text and therefore may help the user to focus on their position on the page. Sheet magnifiers may be designed as full-sized sheets magnifying the whole page or be smaller.
They are sometimes made of plastic and have a relatively low level of magnification, which is determined by the thickness of the lens.
Video magnifiers
A range of video magnifiers are available from hand-held and portable models, models that connect to computers and/or TV screens and desktop mounted models. Advantages of video magnifiers over traditional magnifiers may include:
- the ability to vary the magnification (e.g. from 3x to 60x)
- a variable working distance
- a larger magnifier screen/lens for the same effective magnification
- contrast reversal and a larger field of view.
Studies have suggested that smaller print sizes may be read at faster reading speeds when using video magnifiers compared with traditional magnifiers, but that users may be slower at initially finding the text they are looking for.
Handheld video magnifiers
These provide a magnified image on an integral screen. Most offer a choice of contrast modes and may also have the option of saving or 'freezing' the image (image capture). The magnification range for these magnifiers tends to be limited relative to desktop video magnifiers. The RNIB state that these items are generally suitable for viewing labels, books and newspapers.
Portable video magnifiers
Portable video magnifiers are larger than handheld magnifiers but are still transportable. The screen and camera may be combined or as separate units connected by a cable.
The camera, which is often similar in shape to a computer mouse, is placed on the original image and can be moved across the paper or object while the magnified image appears on the screen.
Video magnifier systems which provide a magnified image when connected to a television or PC screen
These may consist of a handheld camera, similar in shape to a computer mouse, that rests on the original image and can be moved across the paper or object, or may be mounted resembling a desktop lamp with a head which contains the camera and can be angled to focus on the document.
Please check the connection required to the television, as many models require a SCART socket that many newer televisions may not have.
Desktop video magnifiers
Desktop video magnifiers are stood on a desk or work surface. They have the highest magnification compared to other types of video magnifier.
Most have a fixed camera pointed down at a reading table on which printed material can be placed. On most models the table is on rollers so it can be moved up, down and left to right across the page.
The magnified image can be zoomed in and out and adjusted for contrast and colour. Some models can superimpose a line or dot on the screen to help make it easier to follow the text being read.
Magnifying apps
Magnifying apps can be downloaded to compatible smart phones and are designed to give a magnified image on the smart phone's screen. These apps do not have the same performance and features as a handheld video magnifier, but if you do use a smart phone you could try an app before deciding whether to invest in a handheld video magnifier.
Many of these apps work best on later versions of well-known phones with an enhanced autofocus cameras. When downloading an app use only well-known app download markets - they significantly reduce the likelihood of downloading an app malware or virus.
If you're interested in downloading a particular app, run an online search on its name first (using a search engine) to see what others say about it or to check for malware reports.
Electronic reading equipment and audio books
Text to speech scanning machines
Text to speech scanning machines (also called stand-alone reading machines) scan and translate printed text into synthetic speech - you place a book or sheet of text in/on the machine and it will read the text to you. The scanner may be able to read from books, newspapers, magazines and A4 sheets.
Some models can be connected to a screen to give a magnified image of the text as well as speech output. Another function that some models have is the ability to connect to a Braille display to give Braille output of the scanned text.
Alternatively, for users who have a PC with speech output software, it may be a cheaper alternative to buy a scanner and some optical character recognition software (OCR). However, this requires setting up and tends to be slower to use than the purpose built machines. There is also software which can be added to certain mobile phones to give them a reading aid function. The software uses the phone's built-in camera to capture an image of text and then converts it to synthetic speech.
DAISY players
DAISY Players play DAISY audible books and replace the old audio books on cassette format. DAISY is an acronym standing for Digital Accessible Information System and can play/show audio, text and pictures. It makes them accessible to individuals with visual difficulties that affect their ability to read printed material.
DAISY material can be played on a stand-alone DAISY player, or by using DAISY software on a computer. Approximately 25 hours of audio can be recorded on a Daisy CD.
Users of DAISY players can navigate through the recording/book by sections, sub-sections, chapter or pages. Bookmarks can be inserted at any point, and there is a 'resume' option which continues playback from the point the reader last reached (rather than going back to the beginning, which is what happens with conventional CDs).
Tablets and ebooks
Many sites will also provide Ebooks. Ebooks can be read on tablets and ereaders which provide options for enlarging the text. A growing range of tablet and ereader accessories are available including mounts for tablets such as the iPad, and switches and switch interfaces for use with tablets and ebook readers. These switches could, for example, be used to turn the page of an ebook.
Talking books, newspapers and magazines services
Your local library
Your local library is likely to provide a range of audio books and giant print books to loan for free. Speak to your librarian about how to sign up, what titles they have available, and the length of loan available to you.
RNIB Library
The RNIB Library provides a wide range of library and information services for people with sight loss. Resources include talking books, Braille and giant print books, music and online reference services.
RNIB Newsagent
The RNIB Newsagent (formerly National Talking Newspapers and Magazines) provides a wide range of newspapers and magazines for people who find standard print inaccessible. It offers a range of newspaper and magazine titles in a variety of accessible formats, including audio CD or USB, DAISY CD, Braille, large print and online.
Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg is a collection of free electronic books available on the internet. There are currently almost 10,000 books on the site, however these are books out of copyright, generally pre-1923 and so they do not include the latest bestsellers, but do include classic books from authors such as Conan Doyle, Dante, Dickens, Shakespeare, Twain, Verne and Wells. The books can be downloaded to a computer and read with software, or a selection are available as computer-generated eBooks and will play from the Gutenberg site here
Using a keyboard
If you have not learnt to touch type then finding your way around a computer keyboard may be difficult if you have low vision. There are keyboards and accessories which may help you to navigate around the keyboard.
Keytop stickers & keyboard gloves
Keytop stickers can be stuck onto the individual keys on a computer keyboard.
The stickers have large lettering printed in a bold typeface with either black lettering on a yellow background, white lettering on a black background or black lettering on a white background to enhance the contrast.
Alternatively, flexible keyboard gloves are available to fit over specific keyboards with the same large print, bold high contrast lettering as the stickers.
Large print keyboards
These are standard size keyboards with large print on the keys. As with the stickers the keyboards may be available with black letters on a white or yellow background or white letters with a black background.
Keyboards with large keys
These are keyboards with keys which are larger than a standard keyboard.
They often lack the keys which are not used very often, so it is important to check that any keyboard shortcuts (pressing keys together to activate particular functions) you use can still be made on the keyboard.
These keyboards may have the same colour options as the above large print keyboards and may either lay the keys out in the standard QWERTY format or alphabetically.
Braille equipment
Braille is a system of raised dots which people read by feeling with their fingertips. The Braille dots are used to represent words and numbers, punctuation characters and even mathematics, science and music notation.
Braille has many uses with a wide selection of magazines, fiction and non-fiction books available and labelling for items such as food cans and packets, medicines, documents, CDs and games including cards like Uno and bingo. Bank statements, utility bills and other business letters can be provided in Braille and some restaurants and pub chains offer Braille menus.
A Braille character or "cell" consists of 6 or 8 dots. There are different Braille codes in use:
- uncontracted Braille represents each print character as one Braille cell
- contracted Braille is a form of shorthand in which groups of letters may be combined into a single Braille cell.
Many experienced Braille users read and write contracted Braille.
Braille requires a fine sense of touch - some individuals with conditions such as diabetes, who have reduced finger sensitivity, may find using Braille difficult. Moon could be an easier alternative.
Manual Braille equipment
Braille can be produced manually, using a stylus on a portable hand-frame or on a manual desktop machine similar to traditional manual typewriter.
Traditional frames create a dot on the reverse side of the paper so the Braille has to be written back to front.
Upward writing frames are now available which create the dots on the front of the piece of paper enabling you to produce Braille from left to right as you would read the code.
Some manual machines for creating Braille are portable, others are designed as desktop machines, similar to traditional manual typewriters.
They have six keys to produce the Braille (one key for each dot in a Braille cell). Some Braille machines can use standard A5 and other standard paper sizes.
Good practice indicates that Braille should always be written on Braille paper which ensures that the Braille produced will be far more durable.
Some simple manual Braille machines can produce Braille on Dymo tape to create labels. Alternatively, many people use an audio labeller whereby they can affix a small label or dot to an item, use the device to record the information, then use the device to play back the information.
Braille computer equipment
Braille can also be produced on a computer using translation software and a Braille embosser instead of a printer.
A keyboard with Braille keys instead of the standard QWERTY keys can be used, although some users may prefer to continue using a standard keyboard. A Braille display can be linked to a computer to enable a user to read by touch what is on the screen.
If portable computing is required, Braille notetakers are machines with word processing features similar to an electric word processor or laptop, but with a Braille keyboard and / or Braille display.
Braille embossers
Braille embossers print Braille onto special Braille paper, from a computer. They are connected to the computer like a text printer or can be connected to notetakers. The paper is thicker and more expensive than standard printer paper.
Software is required to convert text to Braille before it is printed/embossed (known as Braille translation software).
Embossers can be noisy; if an embosser is going to be used regularly and cannot be kept in a room away from people, an acoustic hood or soundproof case is recommended. Before purchasing a Braille embosser consider issues such as the noise, the speed the embosser is capable of printing at, and whether you need the printer to be portable.
Braille keyboards
These computer keyboards with Braille keys and are different in design to the traditional QWERTY keyboard keys.
Braille displays
Brailler displays are tactile devices that are usually placed in front of your computer keyboard providing you with the means to read the contents of your computer screen by touch in Braille.
Braille displays have a number of cells and each cell has six or eight pins. These pins are electronically moved up and down, to create a Braille version of the characters that appear on the computer screen. Each Braille cell represents one character from the screen. An 80 cell Braille display represents approximately one line of text on a screen.
Before you purchase a Braille display, try several to ensure that the one you choose is comfortable to use and provides the functions you need. Many screen readers offer two outputs: speech and Braille. Depending on your requirements, using the speech output facility of a screen reader will be a cheaper option than harnessing a Braille display to it. We recommend you speak to the RNIB for advice as these devices can be expensive.
Notetakers
This portable device can be used as a word processor to take notes, record and organise information.
Some may also have features to provide a calendar, phone book, internet, email and run Windows based operating systems. They feedback information by speech output or via a Braille display.
Moon
Moon is a system of raised lines and curves that people read by feeling with their fingertips. Moon characters are fairly large and many characters have a strong resemblance to their print equivalent. Consequently, individuals who lose their sight later in life, or individuals who do not have sensitive touch in their fingertips, may find Moon easier to learn then Braille.
Moon can be used to label items such as food cans and packets, medicines, documents, CDs etc. There are books available which are written in Moon, although there are many more books available in Braille than Moon. As Moon is not so well known it is rarely offered as an alternative format for items such as statements, bills and menus.
Moon can be produced using portable hand frames or a computer with a Braille embosser and translation software.
Stationery
Writing frames
Writing frames, into which a piece of paper can be inserted, are available with an elasticated cord acting as line guides.
Paper, envelopes or documents can be inserted into the flat frame to keep you writing within the lines.
They consist of either plastic frames or string lines (which are more flexible and helpful when writing in small case letters with tails such as g, j, p).
Reading Guides
Reading Guides are plastic cards with cut out rows to allow lines of print to be read without glare or confusion from the surround print. They come in various sizes.
There are also options of higher contrasting lined paper to make the lines more obvious for those with low vision, as well as raised lines so they can be felt by the writer.
Telephones and accessories for blind or partially sighted users
Telephones with large keys and/or enlarged numbers
These may be helpful if you have low vision. Some models have keypad buttons with varying shapes to facilitate identification by touch and some have large LCD displays. These features are available on corded, cordless and mobile telephones.
Most push-button telephone keypads have a raised dot on the central five key to help orientate a user relying on touch. Some of the phones in this group have a number of 'one-touch' memory buttons that dial stored telephone numbers.
It may help if other function keys, such as memory keys are separated from and/or shaped differently to the number keys.
Mobile phones
There are models available with an enlarged keypad, emergency button, or a high contrast display with a large font.
Other features can include:
- well-spaced raised buttons
- a large display
- adjustable brightness
- voice dialling.
Telephones with spoken annoucements
There are telephones that speak the numbers entered when dialling, so you can confirm you have pressed the intended keys. Some models can also speak out the number of the caller when receiving an incoming call and/or have a talking phone book and speech guidance to the menu settings.
Models with a LCD display showing callers telephone numbers, or spoken announcement of the number of a caller, require subscription to a caller ID service.
BT’s 195 Directory Enquiries service is free to apply for if you have a visual impairment and once registered, customers can be connected to the number found at the same rate as if you had dialled it yourself.
Accessories
Accessories are also available which dial the telephone for you including voice operated diallers - they are used WITH your existing telephone.
Voice diallers
Voice diallers allow you to dial a number by speaking the name of the person you wish to call. Certain mobile telephones offer voice control as a feature for using the entire telephone as part of the telephone’s integral settings.
It is wise to consult the instruction manual for your particular telephone to identify how to access this facility.
New Technology
A range of new technology for phones and tablets is rapidly becoming available; however, it is worth noting that advice about these items is currently at a general level as the market for this technology grows and personal use of the technology will depend on the type of device you have and its technical ability.
Items specifically include new apps for mobile smart phones and tablets which have, for example, the ability to describe the world around you, assist you with writing emails or messages, reading menus to you in restaurants, provide spoken information on how to get home by train and provide information about station locations, train times and platform numbers. Some are free to download and use and others have a charge for use.
Supply and provision of equipment
Try equipment before you buy
If you decide to buy equipment privately it is best to try and compare the different ranges first. You may have an equipment demonstration centre near you where you can visit to view and try out ranges of equipment. You will receive impartial advice to help you choose appropriately. However, centres may not display examples of all the equipment in this factsheet. You will need to contact your nearest centre to find out what they have and to book an appointment.
Be cautious of sales people who try to persuade you to buy equipment that may not meet your needs fully or is over-priced. Buying from a company that belongs to a trade association, such as the British Healthcare Trades Association (BHTA) may give you some reassurance. BHTA members have signed up to a code of practice governing standards of customer service.
Statutory provision
Eligibility for sensory communication equipment varies depending on where you live. Many local authorities apply eligibility criteria for equipment provision, including assistive technology such as communication equipment. Contact your local authority and ask for information on their communication equipment services. They may arrange for you to receive an assessment. This will examine if you meet their criteria to receive the equipment. Some local authorities may only provide equipment to those with ‘substantial’ or ‘critical’ needs.
If your local authority assess you as requiring communication equipment, they may also complete a financial assessment. This is to assess the level of any contribution you may be required to make. The charges and how they work vary in different areas.
National catalogue prescription scheme
In some areas of the country a prescription scheme for equipment is in operation. There is a 'national catalogue' of equipment that may be provided by prescription, although local areas can choose which of these items they will include in their schemes. This is part of the Department of Health’s Transforming Community Equipment Services (TCES) programme. There is a small range of sensory communication equipment on the national catalogue that can be provided via prescriptions.
If you receive a prescription for one of these items you take your prescription to a local accredited retailer who will provide you with the item. Alternatively you can ‘top-up’ paying extra for an item that does what the specific item prescribed would do, but offers extra features or perhaps you prefer its appearance. The scheme is designed to stimulate and encourage choice and control.
The supply of equipment depends upon the type and extent of your disability, your age and your circumstances. At present, most reading and writing aids are not regarded as a daily living need and are therefore not supplied via a community occupational therapist.
If you are partially sighted, and have some usable sight, it is worth asking your GP or hospital consultant for an assessment at a low vision clinic. These services often provide small reading aids, such as magnifiers or pocket binoculars on a free loan. These are often provided at NHS hospitals, but a few centres are independently run by the Partially Sighted Society. Sometimes smaller items of daily living equipment may be provided by a social worker at your local authority who deals with sensory impairments.
If you are in paid employment and need equipment to assist you with communication at work, you may be entitled to help with the cost and provision of the equipment. This is through the Access-To-Work (ATW) scheme run by the Department for Work and Pensions. It is designed to pay for the additional cost of aids and adaptations needed because of your disability. In some circumstances, a part-time support worker may be funded to perform these tasks if you are unable to do them for yourself.
For children and students
If a child has a disability and is under the age of 18 and still at school, access to funding for equipment may be available if he/she has a statement of special educational needs. For further information contact your local education authority.
If you are a student in higher education, you may be entitled to a disabled students’ allowance. It is awarded by your local authority to cover the additional cost of your disability. If you are a student in further education, you may be entitled to funding through a scheme called the Access To Learning Fund scheme.
Other sources of funding
Charitable trusts may sometimes provide funding for equipment. Charities will only give awards in accordance with a predetermined criteria, so it is important that you carefully select the trusts you apply to.
Most libraries hold directories of suitable funders in their reference section, such as the The Directory of Grant Making Trusts.
The Grants for Individuals website is run by the Directory of Social Change and lets subscribers search for grants, but is intended for organisations searching for funding for individuals. AbilityNet publish a factsheet Funding for an Adapted Computer System which lists possible grant giving trusts. AbilityNet's factsheet also lists possible sources of second hand and refurbished computer equipment.